During this post we’ll cover the essential nutrients that plants require to thrive along with the role these nutrients play in the plants life cycle.
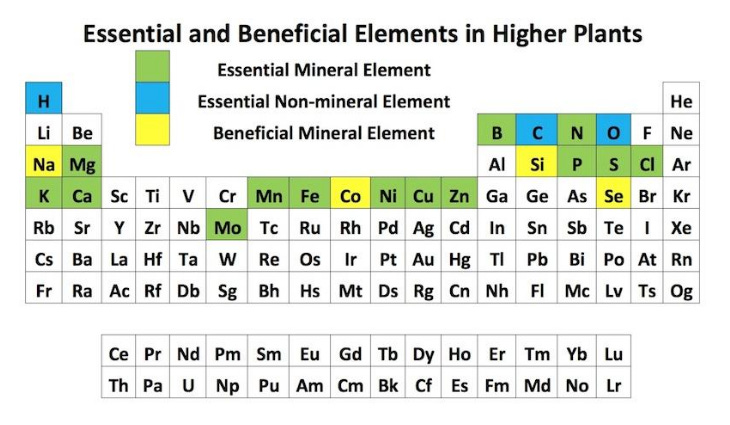
There are seventeen elements known to be necessary for plants to complete their life cycle, the essential elements.
Of the seventeen essential elements, hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and carbon (C) come from the air and water and are readily available. Although nitrogen can also be found in the air, its gaseous form is not useable by plants. Along with nitrogen, the rest of the elements are found in the soil. Depending on the soil properties, however, some of these elements may be present but not in forms that are useable for plant use. Still, some soils may lack one or more of these elements.
When one or more of the essential elements is deficient, plants cannot complete their life cycle. Such deficiency will be expressed in deformed plant growth and supply of the lacking elements will need to be provided in order for the plant to survive.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are essential elements that are required by the plants in large quantities (parts per 100 of dry plant matter). Macronutrients are not more important than the other essential elements, they are simply required in larger quantities.
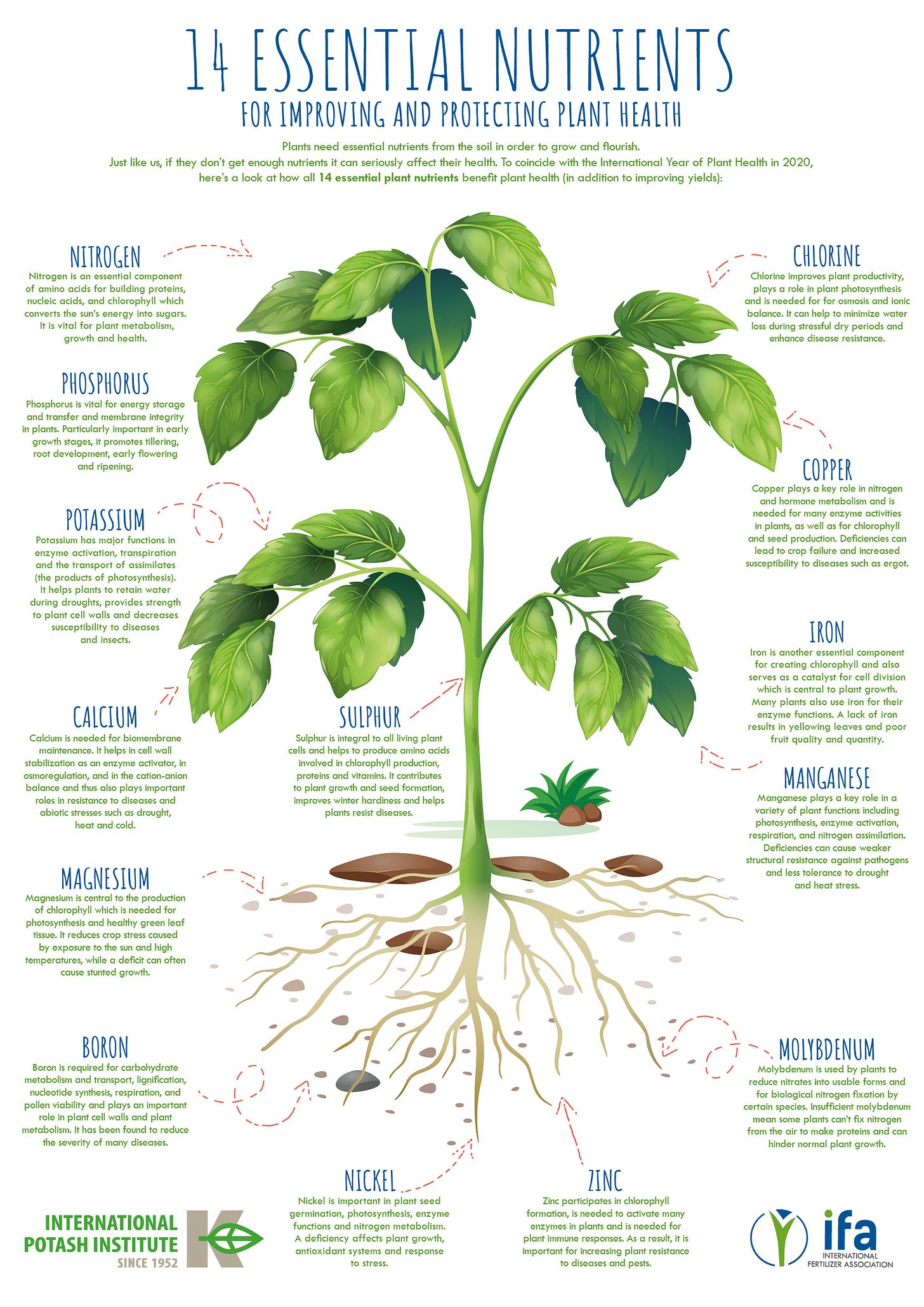
1. Nitrogen (N)
2. Phosphorous (P)
3. Potassium (K)
4. Calcium (Ca)
5. Magnesium (Mg)
6. Sulfur (S)
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, also known as trace elements, are elements that are required by plants in small quantities (parts per million of dry plant matter). Micronutrients should not be mistaken as less important than their macro counterparts.
1. Boron (B)
2. Chlorine (Cl)
3. Copper (Cu)
4. Iron (Fe)
5. Manganese (Mn)
6. Molybdenum (Mo)
7. Nickel (Ni)
8. Zinc (Zn)
There are also other elements that although not essential to plants can be considered beneficial.
Regenerative Landscape Design - Online Interactive Course
Want to learn how to design, build and manage regenerative landscapes? Join us on our Regenerative Landscape Design - Online Interactive Course. We look forward to providing you with the confidence, inspiration, and opportunity to design, build and manage regenerative landscapes, gardens, and farms that produce food and other resources for humans while enhancing biodiversity.
You can access the course material at anytime and join the live sessions and interactive forums that run from May - Oct every year. All members of the Bloom Room receive a 500 EUR discount. To take up this offer all you have to do is become an annual subscribers to our Substack and register here with the promo code BLOOM.
I look forward to you joining !
Beneficial Elements
Beneficial Elements are elements that help optimize the growth and development of plants but they are not essential for growth. When they are absent in the soil, plants can still live a normal life. Here are some criteria that separate beneficial elements from the essential ones:
1. It can compensate for the toxic effects of other elements.
2. May replace mineral nutrient in some other less specific function such as the maintenance of osmotic pressure.
3. May be essential to some but not to all plants.
Examples of beneficial elements are:
Silicon (Si)
Silicon increases the resistance of plants to pathogen and pests. It also increases drought and heavy metal tolerance of plants. Overall it improves the quality and yield of agricultural plants.
Cobalt (Co)
Cobalt is essential for the growth of Rhizobium bacteria for N fixation and thus beneficial for the plant. Nitrogen fixation is the process by which the atmospheric molecular nitrogen (N2) is reduced to form ammonia (NH3). This process is carried out by nitrogen-fixing bacteria which are found in the roots of most leguminous plants. Ammonia is the form of nitrogen that is used by plants and other living systems in the synthesis of organic compounds.
Lithium (Li)
Affects transport of sugars from leaves to roots. Production of food (carbohydrates and sugars) happens in the leaves during photosynthesis. This food will be transported to the different parts of the plant such as the roots, fruits, new shoots, and stems. Lithium enhances the transport of such food to the roots.
Mature compost can provide all the essential and beneficial elements to your garden soil where your plants can access them. Growing certain plants and using them for mulch can also provide more of certain elements that may be needed for certain types of crop production, and I'll be posting more on the details of this in the future.
Fortunately, there is a very simple and effective means to ensuring an adequate supply of these elements to you garden ecosystem, adding Compost :)
Macronutrients - Role in Plant Growth
NITROGEN
· Necessary for formation of amino acids, the building blocks of protein
· Essential for plant cell division, vital for plant growth
· Directly involved in photosynthesis
· Necessary component of vitamins
· Aids in production and use of carbohydrates
· Affects energy reactions in the plant
PHOSPHORUS ·
Involved in photosynthesis, respiration, energy storage and transfer, cell division, and enlargement
· Promotes early root formation and growth
· Improves quality of fruits, vegetables, and grains
· Vital to seed formation
· Helps plants survive harsh winter conditions
· Increases water-use efficiency
· Hastens maturity
POTASSIUM
· Carbohydrate metabolism and the break down and translocation of starches
· Increases photosynthesis
· Increases water-use efficiency
· Essential to protein synthesis
· Important in fruit formation
· Activates enzymes and controls their reaction rates
· Improves quality of seeds and fruit
· Improves winter hardiness
· Increases disease resistance
CALCIUM
· Utilized for Continuous cell division and formation
· Involved in nitrogen metabolism
· Reduces plant respiration
· Aids translocation of photosynthesis from leaves to fruiting organs
· Increases fruit set
· Essential for nut development in peanuts
· Stimulates microbial activity
MAGNESIUM
· Key element of chlorophyll production
· Improves utilization and mobility of phosphorus
· Activator and component of many plant enzymes
· Directly related to grass tetany
· Increases iron utilization in plants
· Influences earliness and uniformity of maturity
SULPHUR
· Integral part of amino acids
· Helps develop enzymes and vitamins
· Promotes nodule formation on legumes
· Aids in seed production
· Necessary in chlorophyll formation (though it isn’t one of the constituents)
Micronutrients - Role in Plant Growth
BORON
· Essential of germination of pollen grains and growth of pollen tubes
· Essential for seed and cell wall formation
· Promotes maturity
· Necessary for sugar translocation
· Affects nitrogen and carbohydrate
CHLORINE
· Not much information about its functions
· Interferes with P uptake
· Enhances maturity of small grains on some soils
COPPER
· Catalyzes several plant processes
· Major function in photosynthesis
· Major function in reproductive stages
· Indirect role in chlorophyll production
· Increases sugar content
· Intensifies colour
· Improves flavour of fruits and vegetables
IRON
· Promotes formation of chlorophyll
· Acts as an oxygen carrier
· Reactions involving cell division and growth
MANGANESE
· Functions as a part of certain enzyme systems
· Aids in chlorophyll synthesis
· Increases the availability of P and CA
MOLYBDENUM
· Required to form the enzyme "nitrate reductas" which reduces nitrates to ammonium in plant
· Aids in the formation of legume nodules
· Needed to convert inorganic phosphates to organic forms in the plant
ZINC
· Aids plant growth hormones and enzyme system
· Necessary for chlorophyll production
· Necessary for carbohydrate formation
· Necessary for starch formation
· Aids in seed formation
NICKEL
-Nickel is a co-factor or a way of helping to initiate the activity of particular enzyme that's important in the metabolism of nitrogen.
As previously mentioned, in addition to the 14 nutrients listed above, plants require carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, which are extracted from air and water to make up the bulk of plant weight.
Applying good compost to your soils will provide all of the nutrients your plants require. For how to make your own compost see our previous post here .
Support Our Project
If you appreciate the work we are doing you can show your support in several ways.
Become a member of the Bloom Room. A $70 annual subscription to our Substack provides you with access to live sessions, design tutorials, a members forum and more, see details here.
Make a purchase of plants or seeds from our Nursery or Online Store
Joining us for one of our Practical Courses or Online Courses
Comment, like, and share our content on social media.
We offer a diversity of plants and seeds for permaculture, forest gardens, and regenerative landscapes including a range of fruit and nut cultivars. We Deliver all over Europe from Nov - March. - Give a happy plant a happy home :)
Welcome to our Online Store where you can find Forest Garden/ Permaculture plants, seeds, bulbs, and Polyculture multi-packs along with digital goods and services such as Online Courses, Webinars and eBooks. We hope you enjoy the store and find something you like. It's your purchases that keep our Project going.
You can also find our full list of trees. shrubs and herbs for forest gardens on our nursery website.







No comments:
Post a Comment